What Are the Benefits of Biological Soil Testing?
This is the second article from Biome Makers in a series all about soil biology. Check out the first article, “What do microbes do in the soil?”
The short answer: Biological soil testing, also known as soil health assessment, offers a holistic view of the soil ecosystem, including abundance, diversity, interactions, and activity of tiny microorganisms. These microbes play a crucial role in breaking down organic matter, cycling nutrients, improving soil structure, and protecting plants from diseases.
Back it up: By understanding the microbial community, land managers can assess the soil’s ability to support plant growth, nutrient cycling, disease suppression, and other important soil functions. In fact, soil microbes perform seven essential functions in the soil, and you can read about them here.
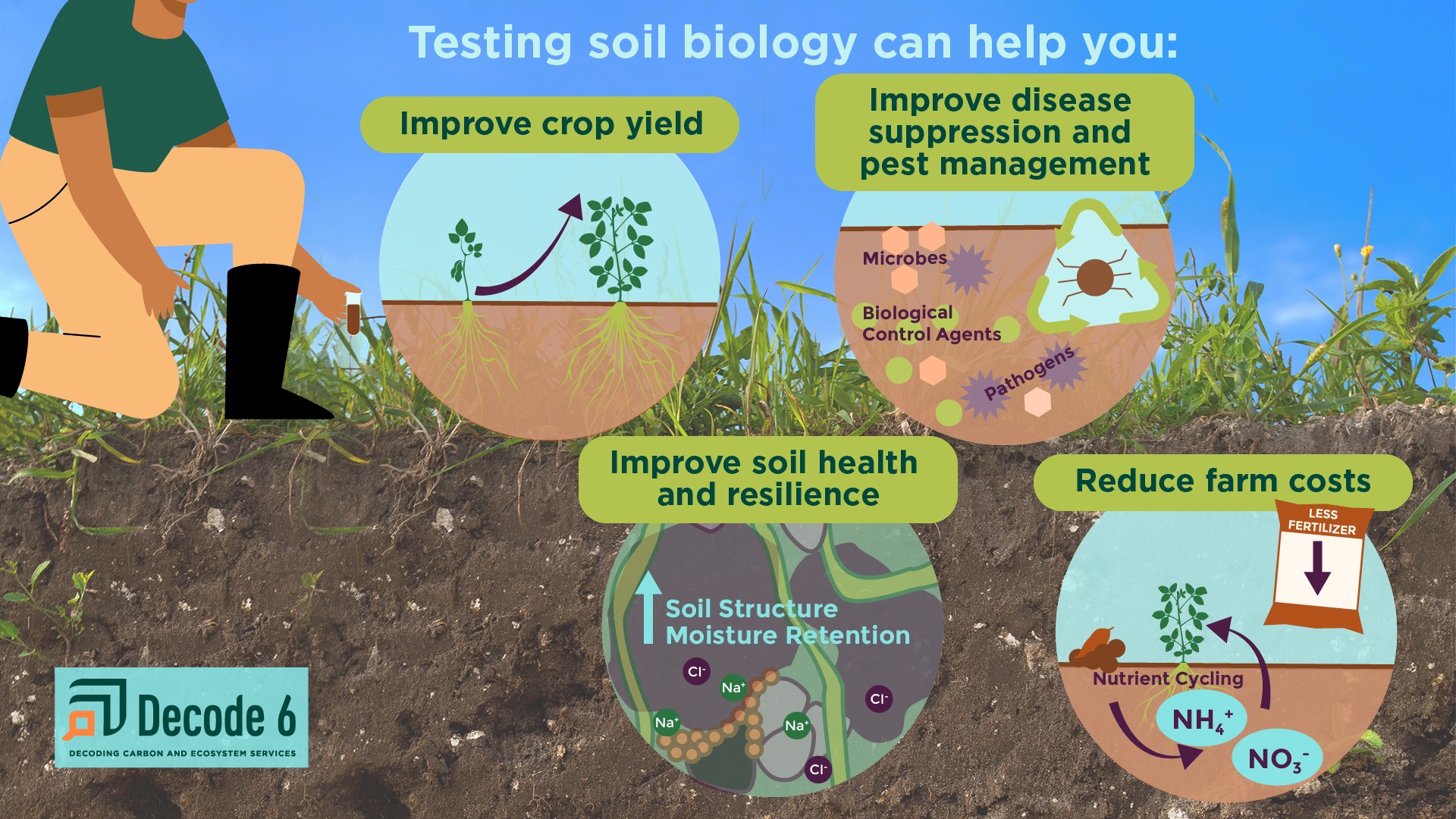
The four benefits of biological soil testing include improved crop yields, disease suppression and pest management, reduced farm costs, and improved soil health and resilience. Graphic by Karen Brey.
Here are four potential benefits of biological soil testing:
- Improved crop yields: Soil testing empowers growers to optimize crop yields by identifying nutrient deficiencies or imbalances that may restrict plant growth.
- Adjust fertilization practices for optimal nutrient mobilization: Soil testing provides valuable insights into nutrient deficiencies or imbalances, allowing growers to tailor their fertilization practices to achieve optimal nutrient mobilization.
- Address stress adaptation: By understanding the factors in the soil that contribute to improved stress adaptation, growers can employ strategies to enhance plants’ ability to adapt to and cope with stress.
- Understand hormone production: Soil testing aids in understanding the soil’s impact on hormone production, which plays a crucial role in plant growth and development.
- Disease suppression and pest management: Identifying the presence of certain diseases or pathogens at early stages, even before symptoms become apparent, enables us to take proactive and efficient actions to combat them, leading to improved effectiveness in our fight against these threats.
- Identify beneficial microorganisms for disease suppression: Biological soil testing provides insights into the presence and abundance of beneficial microorganisms that contribute to disease suppression in the soil.
- Promote eco-friendly pest management practices: By monitoring the microbial composition of the soil over time, growers can observe how adopting suitable management practices (like integrated soil fertility management and integrated pest management, or IPM), influence microbial diversity.
- Reduced farm costs and negative impacts: By optimizing fertilization practices based on soil test results, growers can achieve efficient nutrient management, reducing costs associated with excessive fertilizer use.
- Avoid over-application of fertilizers: Soil testing provides insights into nutrient cycling pathways and levels in the soil, allowing growers to apply fertilizers judiciously and avoid excessive use.
- Optimize nutrient use efficiency for environmental sustainability: Growers can improve nutrient use efficiency, minimizing environmental impacts associated with nutrient runoff.
- Improved soil health and resilience: By enhancing soil resilience, growers can protect their crops, reduce risks, and develop sustainable land management approaches that ensure long-term productivity and environmental sustainability.
- Manage soil health based on soil biology, organic matter content, pH, and texture: This information helps growers identify areas of their fields with different soil characteristics and nutrient needs, allowing for more targeted fertilization and other management practices.
- Improve soil structure and nutrient availability: Implementing soil testing-informed practices like organic matter management, composting, and cover cropping not only improves soil structure and nutrient availability but also contributes to soil resilience. Resilient soil can better withstand drought, heavy rainfall, and other environmental challenges.
- Informed decision-making: Biological soil testing guides soil management decisions, precision farming practices, and environmental monitoring efforts.
- Make informed decisions about soil management practices.
- Identify soil characteristics for targeted fertilization and management.
- Assess the impact of land use practices on soil biodiversity and ecosystem functioning.
In short, biological soil testing is a potentially valuable and cost-effective tool that can help empower growers to make informed decisions regarding soil management practices. Growers can gain insights into soil health, nutrient availability, organic matter decomposition, disease suppression, and the overall functioning of the soil ecosystem.
Editor’s Note, 29 Aug 2023: This article received additional review from New Mexico State University professor Gerald (Jerry) Sims.
Photo courtesy of Biome Makers.








